Knowing your customer personas is crucial for your business, therefore knowing to who you actually sell your product or service isn’t optional. So, get to know who your buyer is.
Sounds easier said than done? It can be if you don’t know where to start. But when you understand how things work and what their purpose is, it will all make sense.
So, while all marketers seem to agree that defining your buyer persona is a must for your brand’s success, many of them are still struggling with knowing exactly where to start. How exactly do you define your buyer persona?
First, let’s start with the basics and understand what a buyer persona stands for in marketing.
Short Summary
- A buyer persona is a detailed profile of your target customer. It covers everything from demographic details to hobbies, interests, desires, and challenges, all presented as though the marketing persona were a real person.
- A customer persona includes demographics (age, gender, income), psychographics (interests, values), geographics (location), behavioral data (buying patterns, brand loyalty), goals, challenges, decision-making process, quotes, technology usage, customer journey insights, and a day in the life.
- Most businesses start with two buyer personas, but if you’re targeting multiple industries, you might want one for each, even if some customers across industries seem similar.
- Buyer Personas are detailed profiles of your ideal customers, covering who they are, their demographics, environment, challenges, and dreams, helping you connect emotionally. In contrast, Jobs to Be Done (JTBD) focuses on the practical steps customers take to achieve their goals with your product or service.
- A negative customer persona identifies individuals who are not a good fit for a business. Key attributes include unprofitable customers, misaligned needs, high support needs, low engagement, price sensitivity, and those with a negative impact on the brand. This helps businesses avoid unproductive marketing efforts.
What Is a Buyer Persona?
A buyer persona is a detailed profile of your target customer. It covers key traits, everything from demographic details to hobbies, interests, desires, and challenges, all presented as though the persona were a real person.
Buyer personas (or customer personas) are key for creating messages, content, and offers that make your brand stand out. They’re a must-have for businesses looking to attract, convert, and keep customers.
By creating customer personas, you get a clear picture of what drives your clients’ decisions every day — their motivations, fears, and personality traits. When you make a few different personas, you can tailor your content strategy to connect directly with various customer groups.
So, why are customer personas important? The goal of a buyer persona is to gain insight into how your most important customer profile thinks, acts, responds and behaves online. Additionally, a buyer persona can help you better understand your customer’s needs and desires as well as how your products or services can meet them.
The Difference Between a Buyer Persona and a User Persona
A buyer persona isn’t necessarily the user of the product, but it can be. For example, if you purchase a bicycle for yourself, you are both the buyer and the user. However, if you buy the bicycle for your child, you are the buyer, but your child is the user. This distinction is vital for effective marketing and product development.
3 key differences between a buyer and a user persona:
- While a buyer persona is the decision-maker responsible for purchasing the product, a user persona is the one who actually uses the product.
- A buyer persona is motivated by factors like cost, value, and overall impact on their organization, in contrast, a user persona is driven by how well the product meets their personal or professional needs.
- Buyer personas are essential for understanding the purchase journey and decision-making criteria, whereas user personas are crucial for mapping out the actual usage and experience with the product.
By understanding what decision-makers need and what end-users want, you can create better marketing campaigns, develop products that are easier to use, and keep your customers happy and loyal.
How Many Buyer Personas Should I Create for My Business?
Most businesses start with two buyer personas, but if you’re targeting multiple industries, you might want one for each, even if some customers across industries seem similar. The truth is that there’s no perfect number of buyer personas for a business—it really depends on what works best for you.
Remember, people are more likely to buy when something feels personally relevant. Also, if you’re into niche marketing—targeting a specific part of a market—it can be really powerful to have detailed personas for those niches.
What Is Niche Marketing?
Niche marketing is all about focusing on a specific subgroup within your broader target audience. You pinpoint this narrower audience by diving deep into research to understand their demographics, interests, desires, pain points, and social media habits.
Once you’ve identified your niche, the next step is figuring out how to customize your promotional strategy based on your ideal customer.
Identifying your buyer personas helps you create targeted content and tailor your ads to engage those most likely to buy your products or services.
For instance, if your persona is a modern, urban mom aged 30-40 who loves a healthy, balanced lifestyle, your ads should clearly appeal to this group. You can customize ads further on platforms like Facebook and Instagram by selecting specific demographics such as location, age, and interests.
Without a well-defined buyer persona, your ads might as well be random, which is inefficient and unlikely to yield good results. The key is to focus your marketing on those who are actual potential long-term customers. Personalized marketing isn’t just nice to have; it’s expected by your customers.
How to Create a Customer Persona for Social Media
Although creating creating buyer personas requires thorough planning and data gathering (a mix of qualitative and quantitative data), don’t worry, you’ll be able to manage.
Building a buyer persona involves several key methods to gather the necessary data:
- Use surveys to do market research and collect demographic and preference data from your customers.
- Speak directly with customers, including both regular buyers and those who have stopped using your services, to gain deeper insights.
- Collect insights from your sales team about their interactions with customers.
- Regularly review customer feedback and support tickets for direct insights.
- Analyze follower demographics and engagement using social media tools.
What you need to understand is that in order to properly promote and sell more of your product, reach a larger audience, and grow your list of followers, you need to become very efficient in your marketing strategy and the way to do that is to learn how to create a buyer persona.
Here are a few simple steps to follow when creating your buyer persona:
Step 1: Prepare a List of Questions
Put together a list of relevant questions to ask about each buyer persona you create.
Don’t skip this part as you’ll be surprised to see how many relevant little details you can find out by asking even the most simple questions about your marketing personas.
TL;DR – Here is the information you need to create your customer persona:
- What is your customer’s age, gender, and location?
- What is your customer’s marital status and family structure?
- Where does your customer work, and what do they do there?
- What’s your customer’s job title and description?
- What level of education has your customer achieved?
- What’s your customer’s income like?
- Where do they like to hang out?
- Who influences your customer’s choices?
- What brands does your customer stick with?
- Why do they stick with certain brands?
- What does your customer’s household look like?
- What does your customer like to do for fun?
- Where does your customer work and what do they do there?
- What challenges does your customer face that you can help with?
- What worries your customer the most?
- What’s your customer aiming for?
- What inspires your customer?
- What are your customer’s primary needs and desires?
- Why might someone who fits your ideal customer profile not buy from you?
- Where does your customer spend time online and which social platforms do they prefer?
- Why does your customer shop online?
- Why might they prefer shopping in-store?
- How comfortable is your customer with technology?
- How does your customer like to interact with businesses?
- Which online or social media channels does your customer use and why?
- How often do they use each social platform or online channel?
- What type of content do they engage with the most on these platforms (e.g., videos, articles, images, infographics)?
- What time of day are they most active on these social platforms?
- Do they follow any influencers or brands? If so, which ones and why?
A. Demographics and Professional Information
To create a buyer persona, you need to start with the basics. These questions help you get a clear picture of who your customers are, their background, education, financial status, and what they do for a living.
- What is your customer’s age, gender, and location? (helps tailor marketing strategies and product offerings to match their demographics)
- What is your customer’s marital status and family structure? (provides insights into their lifestyle and spending habits.
- Where does your customer work, and what do they do there? (reveals their daily routine and lifestyle.
- What’s your customer’s job title and description? (indicates their influence and work responsibilities)
- What level of education has your customer achieved? (helps tailor the complexity of your message and product)
- What’s your customer’s income like? (allows you to align your pricing and offers with their financial situation)
- Where do they like to hang out? (understanding their favorite spots, both online and offline, helps target them effectively)
B. Influences and Preferences
Next, let’s dive into what makes your customer tick. These questions help you understand who and what influences their decisions and the brands they love.
- Who influences your customer’s choices? (find out who and what guides their decisions, from influencers to brands and media)
- What brands does your customer stick with? (understand their brand loyalty and see how your brand can connect with them)
- Why do they stick with certain brands? (discover the values and service levels that attract them)
C. Lifestyle and Environment
Understanding your customer’s daily life and environment is crucial. These questions will help you learn about their household, hobbies, and work life.
- What does your customer’s household look like? (get to know who they live with and what their daily environment is like)
- What does your customer like to do for fun? (identify hobbies or interests to see how your products or services fit into their lifestyle)
- Where does your customer work and what do they do there? (this helps you understand their daily routine and lifestyle)
D. Challenges and Pain Points
Knowing your customer’s challenges helps you align your products and services with their needs. Additionally, their primary needs and desires are key to positioning your products as solutions. Addressing these issues can turn them into loyal customers.
- What challenges does your customer face that you can help with? (identify specific problems where your offerings can make a difference)
- What worries your customer the most? (knowing their fears can guide how you reassure them in your messaging)
- What’s your customer aiming for? (align your products with their personal or professional goals)
- What inspires your customer? (understand their aspirations to connect on a deeper level)
- What are your customer’s primary needs and desires? (know what keeps them up at night and help them achieve their goals)
- Why might someone who fits your ideal customer profile not buy from you? (identify and eliminate obstacles that prevent them from using your products or services)
F. Online Behavior
Understanding where your customer spends their time online and their shopping preferences is essential for effective digital marketing. These questions help identify the platforms and experiences they value most.
- Where does your customer spend time online and which social platforms do they prefer? (this helps you decide where to focus your online marketing efforts)
- Why does your customer shop online? (understand their preferences for convenience or why they value online shopping)
- Why might they prefer shopping in-store? (insights into their desired experiences can enhance how you serve them)
G. Interaction and Technology
Knowing how your customer interacts with businesses and their comfort with technology helps you optimize communication and engagement. These questions focus on their preferred interaction channels and digital engagement.
- How comfortable is your customer with technology? (this helps you understand how digitally engaged they are.
- How does your customer like to interact with businesses? (optimize customer interactions and support by using their favored channels like email, chat, calls, etc.)
H. Social Media/Online Use
Being aware of the social platforms and online mediums your customer uses helps you target your marketing efforts effectively. Knowing where they get their information and why they prefer certain platforms can refine your digital strategy.
- Which social platforms and online channels does your customer use and why? (know where they get their information, including favorite websites, books, news outlets, and social platforms)
- How often do they use each social platform or online channel? (allows you to align your posting schedule with their usage patterns, maximizing the chances that your content will be seen and engaged with)
- What type of content do they engage with the most on these platforms (e.g., videos, articles, images, infographics)? (understanding the types of content your audience prefers, helps you create more engaging and relevant content that resonates with them)
- What time of day are they most active on these social platforms? (knowing when your audience is most active allows you to schedule your content during peak activity times)
- Do they follow any influencers or brands? If so, which ones and why? (this information can help you collaborate with the right influencers and brands, enhancing your credibility and reach within your target market)
Step 2: Gather the Data You Need
Your buyer persona research approach will depend on whether you have existing customers or not.
How to Create Buyer Personas Without an Established Customer Base
To gather customer insights when you don’t have customers yet, check out your competitors’ social media and reviews for useful data. You can also browse Quora and Reddit to see what questions people are asking and what they need.
A. Analyze Your Competitors’ Social Media Platforms
Gather demographic and psychographic insights by reviewing the comments and engagement on your competitors’ social media pages. Look for information about the audience’s interests, needs, pain points, activities, education, and other demographic details.
B. Examine Competitor Reviews
Investigate Amazon product reviews, particularly the profiles of reviewers, to understand their interests, buying habits, and the problems they face. Focus on 1-star and 5-star reviews to learn what people love or hate about similar products or services.
C. Use Platforms like Quora and Reddit
Search for questions your potential customers might ask and review the responses. Analyze the tone of voice, attitude, and shared content to understand the audience’s needs and pain points. This information will help you develop your product or service to meet these needs.
How to Create Buyer Personas With an Established Customer Base
To gather customer insights from your existing customer base, chat with your customers, work with your sales and marketing teams, send out online surveys, and use social media analytics. These steps will help you get a better understanding of your customers and improve your strategies.
A. Interview Existing Customers
To get a better understanding of your buyer personas, try talking directly to your customers through interviews and focus groups. Use a set of questions during customer interviews—whether face-to-face, over the phone, or online—to learn about their needs and experiences.
Also, set up focus groups where small, diverse groups can discuss your products or services. A moderator will guide these chats to dig into their opinions and direct customer feedback.
Combining what you learn from both interviews and focus groups will help you spot trends, test new ideas, and fine-tune your buyer personas, making your marketing strategies more effective.
B. Collaborate with Your Sales and Marketing Team
Consult your sales and marketing colleagues to gain insights about the people who purchase your products or services.
C. Conduct an Online Survey
Utilize tools like Jotform Survey Maker, TypeForm, 123 Form Builder, AYTM, Crowd Signal, or SurveyMonkey to create and distribute online surveys.
D. Utilize Social Media Platform Analytics
Leverage the built-in analytics of platforms you already use like Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, and Pinterest to gather relevant data.
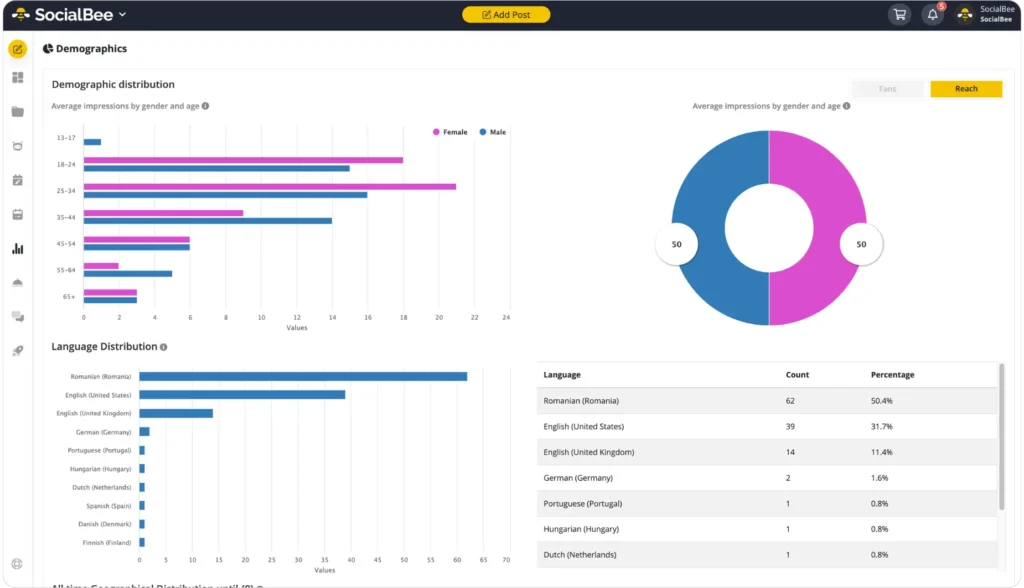
If you don’t have the time to manually switch between platforms to gather insights and create reports, SocialBee can help. Not only can you create, schedule, and share your content from the platform, but you can also monitor your content performance and get insights into your target audience demographics from one place.
The best part? You can generate PDF visual reports in seconds to better understand important data and share them with your team and clients with ease.
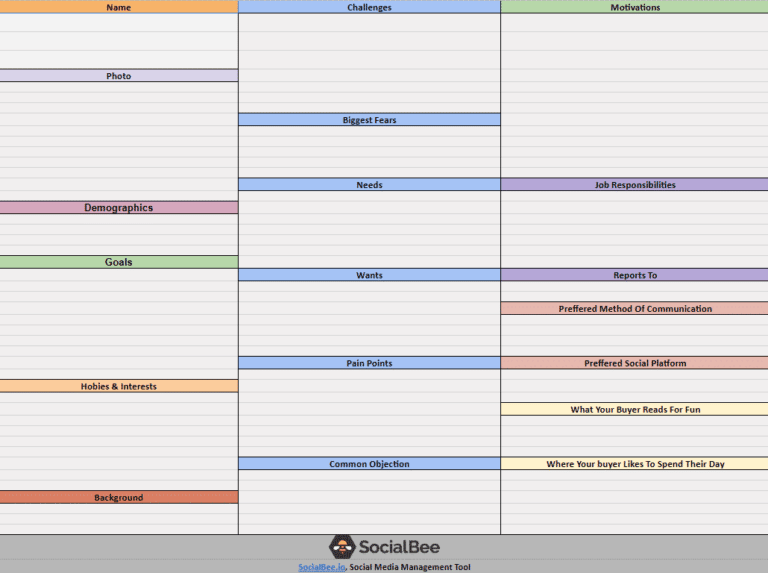
Step 2: Use a Customer Persona Template
Using a template may prove extremely valuable in the process of creating your buyer persona and will help you define your ideal buyer faster and easier.
So, try out our Buyer Persona Template as it’s very easy to use – all you need to do is fill out the Buyer Persona Template sheet step-by-step and you are done. You have your Buyer Persona.

Here are some other buyer persona template samples you could choose from:
- ‘Persona Templates’ from HubSpot
- ‘The Customer Avatar Worksheet’ from Digital Marketer
- ‘User Persona Template’ from Xtensio
- ‘Buyer Persona Template’ from Demand Metric
- ‘The Inbound Marketer’s Pocket Buyer Persona Kit’ from iMPACT
Customer Persona Examples
Now that you know what a customer persona is and how to create one, let’s look at some buyer persona examples to better understand how it looks in practice.
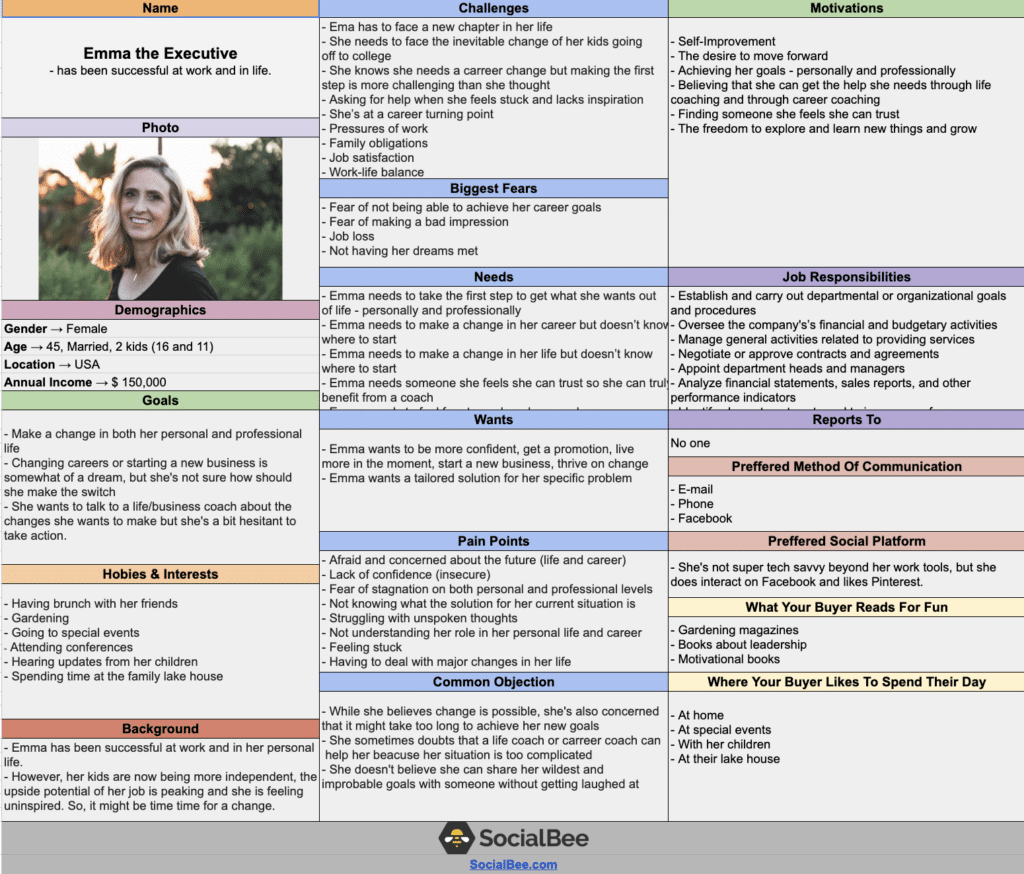
Customer Persona Examples: Emma the Executive
Emma’s template gives a complete picture of her life, both at work and at home. It nails down her challenges, fears, and what drives her, making it super clear what she needs.
The template also highlights her goals and what might hold her back, which helps in crafting messages that really speak to her.
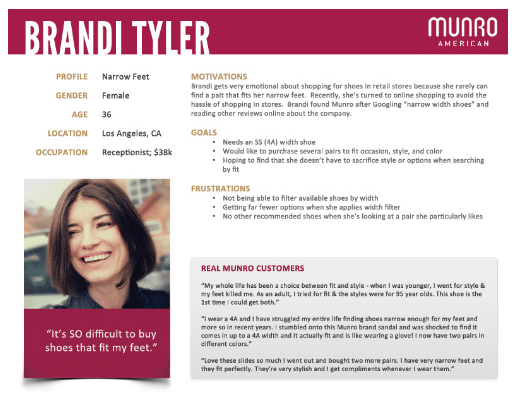
Customer Persona Examples: Brandi Tyler
Brandi’s template captures her emotional struggles and practical needs.
Image Source: Indie Game Girl
Including real customer quotes makes it relatable and easy to understand her perspective. It clearly states what she wants in products, helping you design solutions that fit her needs perfectly.
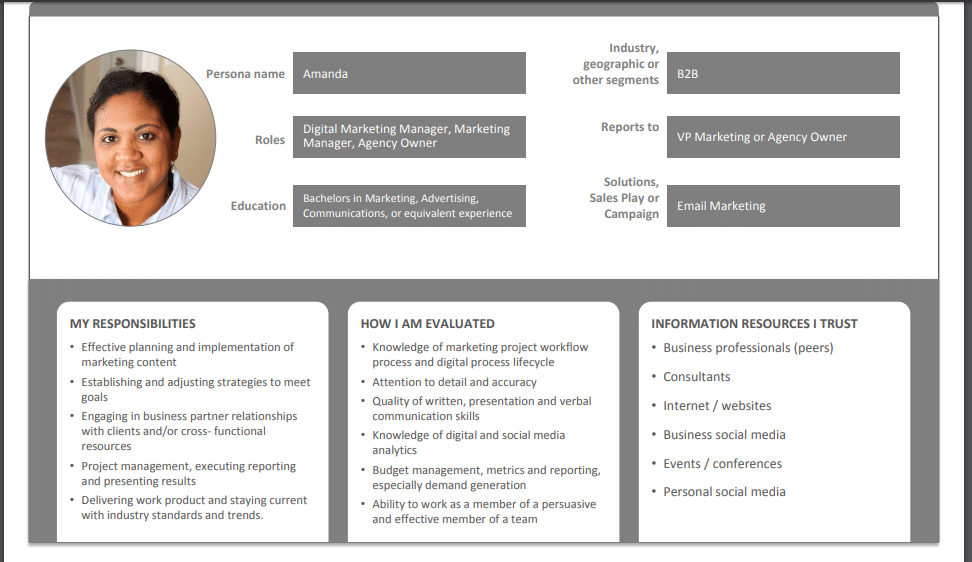
Customer Persona Examples: Amanda the Digital Marketing Manager
Amanda’s template provides details about her job responsibilities and how she’s evaluated.
Image Source: Buyer Persona Institute
This helps you understand her professional mindset and what she values. It also lists where she gets her information, making it easier to know where to reach her and what kind of content she’ll trust.
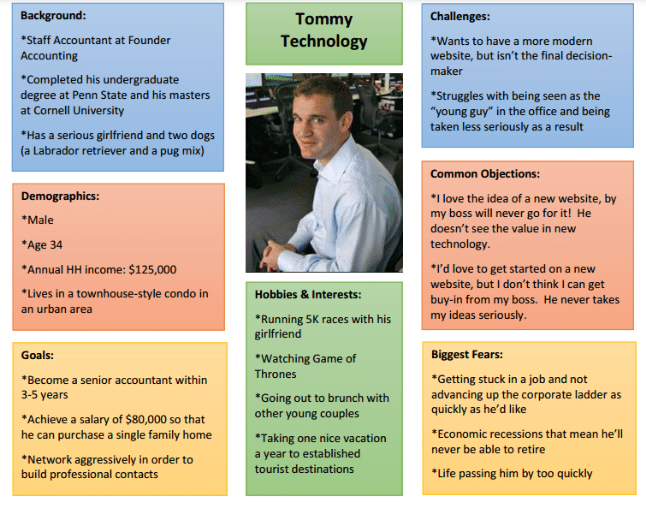
Customer Persona Examples: Tommy Technology
Tommy’s template does a fantastic job of balancing his career goals and personal interests. It clearly shows what he’s struggling with and what he fears the most.
Image Source: Single Grain
The common objections section is great for understanding what might make him hesitate, so you can address those points directly.
Customer Persona Examples: Hulk Hogan, Chief Marketing Officer
This buyer persona shows a CMO, Hulk Hogan, who needs CRM software and content management tools.
Image source: HubSpot’s Free Buyer Persona tool
Businesses can use this to create targeted marketing that addresses their needs and communication preferences. By understanding his job responsibilities, age, education, and tool requirements, companies can develop content that speaks directly to his pain points and deliver it through his preferred channels (email, social media, face-to-face).
How to Use Facebook to Build Buyer Personas
Over 200 million small businesses use Facebook Pages to connect with customers, so you have a real opportunity to find and understand your prospective customers by using the platform.
By tracking what your audience likes and how they interact on Facebook, you can get a good sense of their interests. Facebook’s tools like Events, Groups, and Shops give you extra insights into who’s buying your products or signing up for your events.
Use this info to adjust your offerings and communications to match what your audience prefers. Send them relevant deals or updates directly, and you’ll keep them engaged and more likely to make repeat purchases. Keep it relevant and straightforward to maintain their interest
Here are the key metrics tracked by Instagram Analytics:
- Page Insights: This includes detailed metrics about your page’s performance, such as total likes, reach, engagement rate, and demographic data about your audience. It helps you understand who your audience is and how they interact with your content.
- Post Insights: This provides data on individual post performances, showing what type of content (photos, videos, status updates) performs best in terms of engagement, reach, and interaction.
- Video Insights: For video content, Facebook provides metrics such as the number of video views, average watch time, and retention rates. This helps content creators understand what type of content keeps the audience engaged.
- Group Insights: Tailored for group admins, these insights include membership growth, engagement metrics detailing posts, comments, and reactions to understand content engagement, and identification of top contributors.
- Event Insights: Event organizers can access data such as response statistics showing how many people viewed, responded interested, or confirmed attendance, engagement details on shares, comments, and likes, and demographic data of attendees to better tailor future events.
- Shop Insights: For Facebook Shops, insights include sales performance metrics like overall sales and popular products, customer interaction data detailing how customers interact with the shop, and analysis of traffic sources to understand where visitors are coming from.
- Ad Insights: If you run ads, Facebook offers analytics related to the performance of your advertisements. This includes impressions, click-through rates, conversion rates, and the cost per result. It allows you to see how effectively your budget is being used and to adjust your strategies accordingly.
To learn more about your LinkedIn audience use the following strategies:
- Look at the audiences of your competitors’ pages. This can give you insights into their followers’ interests and demographics.
- Participate in Facebook Groups relevant to your industry. Observe discussions and identify common pain points and interests.
- Use Lookalike Audiences for your ads to find people on Facebook who are similar to your best existing customers. This helps expand your reach to potential new customers who are likely to be interested in your brand.
- Implement the Facebook Pixel on your website to track visitor actions. This helps you understand how your audience interacts with your site and can be used to retarget ads to those users.
- Create ads that dynamically change content to match the interests of each viewer, based on their past interactions and behavior. Use dynamic ads to show personalized product recommendations from your catalog to users who have shown interest in those products.
How to Use Instagram to Build Buyer Personas
Instagram is great for creating personas because it offers relevant information about users’ interests, behaviors, and demographics. By checking out engagement like likes and comments, you can see what your audience loves and tailor your marketing to match their vibes.
Here are the key metrics tracked by Instagram Analytics:
- Follower growth: Spot trends in new followers to understand what attracts them. This helps define what your audience likes.
- Reach and impressions: See how many people are viewing your content to gauge overall performance and refine audience interests.
- Profile visits: Measure interest in your brand to understand what drives curiosity and engagement.
- Demographics: Get details on your audience’s age, location, and gender to create more accurate personas.
- Interests: Know what your followers like to tailor content that resonates with them.
- Post performance: Check which posts (photos, videos, Reels) get the most likes, comments, shares, and saves. This tells you what content your audience enjoys.
- Engagement timing: Find out the best times to post based on when your audience is most active.
- Views and engagement: Track how many people view and engage with your stories. This shows what keeps your audience interested.
- Tap-through and exit points: Learn where viewers lose interest or continue engaging. This helps refine your content to match audience preferences.
To learn more about your LinkedIn audience use the following strategies:
- Collaborate with influencers whose followers match your target audience. Analyze the demographics and engagement of these followers to gain insights.
- Host live sessions where you can directly interact with your audience. Encourage viewers to ask questions and share their opinions.
- Use shoppable posts to tag products and analyze which items attract the most clicks and purchases.
- Review Instagram Shopping insights to understand the purchasing behavior of your followers.
- Utilize Instagram Ads Manager to run targeted ad campaigns. Analyze the performance and audience insights from these campaigns. Create lookalike audiences based on your most engaged followers to find new potential customers with similar characteristics.
- Research and use hashtags relevant to your industry to find and engage with potential customers outside your immediate follower base.
- Leverage social listening to monitor mentions, comments, and DMs to see what people are saying about your brand. This helps you understand their needs and preferences even better, making your marketing more on point.
With SocialBee’s Social Inbox, you can save time by having all your Instagram interactions—mentions, comments, and DMs—in one place. This helps you easily monitor what people are saying about your brand, understand their needs, and engage with them quickly and effectively.
How to Use X (Twitter) to Build Buyer Personas
Building buyer personas using X (Twitter) can be super effective if you know how to dig into the right data.
Start by using X’s analytics to collect data and complete the information by doing your own research on the platform.
Here are the key metrics tracked by X (Twitter) Analytics:
- Engagement rate: Measures the percentage of viewers who interacted with your post (likes, comments, shares, etc.).
- Follower count: Tracks the total number of followers and any changes over time.
- Top Posts (Tweets): Identifies the tweets with the highest number of impressions during a specific period.
- Monthly Impressions: Shows the total number of times your posts were seen in a month.
- Link Clicks: Counts how many times links in your posts were clicked.
- Shares (Retweets): Tracks the number of times your posts were shared on other profiles.
- Replies: Measures the number of comments or quoted retweets your posts received.
PRO TIP: To gather data more easily, use tools like SocialBee and Twitonomy and get insightful information about the content your audience loves in a visual format.
To learn more about your X (Twitter) audience use the following strategies:
- Create lists of people who fit your target audience. Watch what they tweet about to get a sense of their interests and concerns. Check out your followers’ bios to gather information like job titles, hobbies, and location.
- Twitter hashtags are great for finding personas. You could check some general hashtags that your industry is interested in like #Marketing #StockAdvisor or #BeginnerInvestment if you give advice on how to invest, and find the people who are interested in this particular topic.
- Get involved in discussions. Ask questions, run polls, and get feedback. This will help you understand your audience on a more personal level.
- Look at what kind of posts get the most love. Is it videos, images, or maybe just text? What topics get the most engagement? Use this info to see what resonates with your audience.
- Check out who’s following your competitors and what they’re doing right (and wrong). This can help you figure out what works in your niche.
- By looking at the accounts your audience follows, you can learn a lot about their interests and preferences. Just visit their profile and click on the ‘Following’ button.
How to Use LinkedIn to Build Buyer Personas
Using LinkedIn to create buyer personas is super valuable because it gives you access to tons of real, up-to-date info about your target audience. You can check out profiles to see what jobs they have, their skills, and what they’re interested in. Plus, LinkedIn’s analytics can show you what kind of content they engage with.
Here are the key metrics tracked by LinkedIn Analytics:
- Content: Checks how well your posts and videos are doing.
- Followers: Looks at who follows you and where they come from.
- Visitors: Shows details about people visiting your page and how to turn them into followers.
- Leads: Gathers info from people who filled out lead forms.
- Competitors: Compares your page’s performance with competitors.
- Employee Advocacy: Measures engagement with content shared by employees.
- Employer Brand: Tracks interaction with your Career Pages.
- Newsletter Analytics: Reviews how your newsletters perform and who reads them.
To learn more about your LinkedIn audience use the following strategies:
- Use LinkedIn’s search to find profiles that fit your ideal customer or even find the perfect candidates for your job postings. Look for specific job titles, seniority levels, and industries. This will help you understand who your audience persona is, what they do, and what they care about.
- Check out the profiles you’ve found for key insights – look at their skills and endorsements to see what they’re good at and what people recognize them for. Check the groups and associations they’re in to understand their interests and professional networks.
- If you have a LinkedIn company page, use the analytics to learn about your followers and what content they like. This data is gold for refining your personas.
- Take advantage of LinkedIn’s survey and poll features. Ask your network or group members directly for their opinions. This feedback can help validate your assumptions and uncover new valuable insights.
- Connect with and follow industry thought leaders. Their posts and interactions can give you a deeper understanding of industry trends and challenges that matter to your personas.
How to Use Google Analytics to Target Buyer Personas
Google Analytics (GA) is great for figuring out who’s visiting your website and where they’re coming from. It also helps you see how much traffic your social media channels are bringing in.
Here are the Google Analytics website analytics that help you better understand potential buyers:
- Demographics: Find out the age, gender, and language of your users to see who’s interested in your offerings.
- Interests: Learn what hobbies or products catch your visitors’ attention.
- Location: Discover where your visitors come from, right down to the city level.
- Traffic Sources: Identify how visitors arrive at your site, whether through search engines, social media, or directly.
- User Behavior: Observe which pages they visit and how long they stay, which helps you understand what keeps them engaged.
Bottom Line: Crafting your buyer persona isn’t about guesswork; it’s about leveraging real, actionable data from Google Analytics. This data helps you understand your customers’ preferences and behaviors, enabling you to deliver solutions that they genuinely need and want.
What Is the Jobs to Be Done Framework?
A “job to be done” is a concept that pushes you to think beyond just making current solutions better. It’s about designing with the customer’s needs and desires in mind. Simply put, buyer personas tell you who your customers are, while Jobs to be Done tells you why and what they need.
The Jobs To Be Done (JTBD) framework helps you focus on desired outcomes customers want to achieve rather than just the features of your product. It’s about understanding and solving customer problems, which leads to real outcome-driven innovation.
According to Zenkit, “Jobs-to-be-Done, or JTBD for short, follows the idea that customers purchase products or services to get jobs done, not for the products or services themselves.”
And here’s how the Christensen Institute breaks down what JTBD is: “The Jobs to be Done framework is a tool for evaluating the circumstances that arise in customers’ lives. Customers often buy things because they find themselves with a problem they would like to solve. With an understanding of the ‘job’ for which customers find themselves ‘hiring’ a product or service, companies can more accurately develop and market products well-tailored to what customers are already trying to do.”
Image via TwoOctobers
Bottom line: According to the Jobs to Be Done theory (or JOBS theory), customers don’t care about your product or service; they care about getting their job done. Understanding both the jobs customers want to solve and your buyer personas gives you a clear picture of who is using your product and what they’re trying to achieve.
This leads to better products and marketing strategies as well as increased customer satisfaction and better innovation processes.
Now that you know what JTBD is, let’s discuss…
The Difference Between Buyer Personas, Jobs to Be Done, and Customer Journey Maps
Buyer Personas are detailed profiles of your ideal customers, covering who they are, their demographics, environment, challenges, and dreams, helping you connect emotionally. In contrast, Jobs to Be Done (JTBD) focuses on the practical steps customers take to achieve their goals with your product or service.
Bringing these concepts together, Customer Journey Maps show the whole experience your customers have with your product or service over time. They combine the emotional and practical aspects, giving you a full picture of your customer’s journey from start to finish.
Do you need all three?
Without buyer personas, JTBD might miss the emotional and social sides of your customers’ needs, making your analysis too dry and functional. Without JTBD, buyer personas might get too vague or overly specific, causing a loss of focus. And without customer journey maps, you might get lost in the details and lose sight of the bigger picture.
Integrating JTBD and Buyer Personas
Some people say JTBD can replace buyer personas, but that’s not quite right. So why are buyer personas important?
You need both to design a great user experience. JTBD alone doesn’t cover your customers’ motivations, challenges, and pain points. You need buyer personas for that deeper understanding.
Marketing is also key. A great product or service still needs good marketing. Knowing your audience through personas helps you market effectively.
Plus, one product can serve many purposes. Think of a laptop for instance. You can have a buyer persona who wants a laptop for photo and video editing, another who wants to use the laptop for remote work video games, and another for blogging and writing. And so on.
In short, using buyer personas, JTBD, and customer journey maps together gives you a well-rounded strategy to meet your customers’ needs effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
A negative customer persona identifies individuals who are not a good fit for a business. Key attributes include unprofitable customers, misaligned needs, high support needs, low engagement, price sensitivity, and those with a negative impact on the brand. This helps businesses avoid unproductive marketing efforts.
A customer persona includes demographics (age, gender, income), psychographics (interests, values), geographics (location), behavioral data (buying patterns, brand loyalty), goals, challenges, decision-making process, quotes, technology usage, customer journey insights, and a day in the life.
Typically, businesses create between 3 to 5 personas to cover each major customer segment of their audience.
Ready to Create Customer Personas for Your Brand?
By knowing your customers’ backgrounds, interests, and challenges, you can tailor your marketing, develop products that truly meet their needs, and improve their overall experience with your brand.
Combining these personas with the Jobs to Be Done (JTBD) framework helps you understand not just who your customers are, but also why they need your products. This way, you cover all bases, from their emotions to practical needs.
Use insights from social media, competitor research, and customer feedback to make your personas as accurate and useful as possible.