The YouTube algorithm determines which videos get seen, which YouTube channels grow, and how video content reaches new audiences in 2026. Publishing consistently is no longer enough. If your videos do not align with how the YouTube algorithm works, they will struggle to surface, no matter how much effort you put into them.
Unlike other social media algorithms that prioritize fast novelty, YouTube focuses on long-term viewer behavior. It looks at watch history, satisfaction signals, and session patterns to predict what each viewer wants to watch next. That is why some videos continue getting views for years, while others disappear within days.
In this article, I’ll explain how YouTube ranks videos in 2026, where recommendations appear across the platform, how the YouTube Shorts algorithm works, and what actually influences organic reach today.
Plan your posts in no time with hundreds of post ideas and Canva templates.
We’re SocialBee LABS SRL, part of WebPros. We use the information you provide to share relevant content and product updates, as outlined in our Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
Short summary
- The YouTube algorithm decides which videos users see by predicting what each particular viewer is most likely to enjoy watching next.
- YouTube prioritizes long-term viewer satisfaction over short-term spikes, using signals like watch time, average view duration, and direct user surveys.
- The algorithm ranks videos differently across Home, Suggested, Search, and Shorts, with each surface optimized for a different type of viewer intent.
- Suggested videos drive the most YouTube views, relying on videos watched together, topic clustering, and patterns from the same creator.
- Search results behave more like Google search results, rewarding clear video titles and descriptions, captions, and strong watch time from search traffic.
- The YouTube Shorts algorithm relies on rapid signals such as completion rate, rewatch behavior, and early swipe-through patterns.
- Evergreen videos and long-form content benefit from long-term relevance, with older videos often resurfacing when interest returns.
- Accessibility signals like closed captions, multiple languages, and multiple audio tracks help YouTube route content to new global audiences.
- Creators improve organic reach by focusing on clarity, consistency, and relevance, not by trying to game the algorithm.
- Supporting YouTube content across other platforms and maintaining a consistent schedule helps reinforce visibility and viewer habits over time.
What is the YouTube algorithm?
The YouTube algorithm decides which videos users see, based on relevance, viewer satisfaction, and predicted watch behavior. The algorithm accounts for 70% of what users watch on the platform.
YouTube’s core goal is simple. It wants viewers to enjoy watching and keep coming back. The platform is not focused on pushing videos randomly or rewarding short spikes in attention. It prioritizes content that keeps viewers satisfied over time.
At its simplest, the YouTube algorithm works by predicting what each particular viewer wants to watch next. It uses watch history, search history, and user behavior to decide which video should follow the current video. That is why the same video can perform well for one audience and poorly for another.
This is where YouTube differs from other platforms. TikTok and Instagram reward fast, bite-sized novelty. YouTube focuses on session time and depth. It looks at whether viewers watch more than one video, move to related videos, and return later. That focus explains why long-form videos and evergreen content still perform well.
Next, we’ll look at how the YouTube algorithm ranks videos in 2026, including the signals that matter most for visibility and reach.
How the YouTube algorithm works in 2026
In 2026, the YouTube algorithm does not rely on a single signal or a simple score. It evaluates how a video performs with viewers, how satisfied those viewers feel afterward, and how well the video fits into each person’s viewing habits. The goal is to recommend videos that feel relevant now and still make sense later, not just videos that spike briefly.
“It’s not about luck or hacks or how many subscribers you have. It’s about proving through each test phase that this video is good enough, and it deserves to be shown to more and more new people,” says Dan the creator, founder of the YouTube Wealth Academy.
Below are the major categories of ranking signals YouTube uses today:
- Viewer engagement signals
- Viewer satisfaction signals
- Personalized recommendations and user context
- Long-term relevance and topic durability
- Multi-language and global audience optimization
1. Viewer engagement signals
Viewer engagement shows how people react once a video is presented to them. These signals help YouTube understand whether a video attracts attention and holds it.
Key engagement signals include:
- Click-through rate, which reflects how well titles and YouTube thumbnails set expectations
- Watch time, which shows how long viewers spend watching
- Average view duration, which reveals how much of the video is actually watched
- Likes, comments, and shares, which add context but are secondary to viewing behavior
- Return viewers, which indicate whether people come back to the same YouTube channel or continue watching more videos from the same creator
Click-through rate gets viewers to start watching, but watch time and average view duration determine whether the video performs over time. The return viewers metric is especially important because it signals trust and consistency. When videos lose viewers early, YouTube usually stops pushing them, even if they start strong.
2. Viewer satisfaction signals
Viewer satisfaction YouTube signals go beyond visible engagement. YouTube uses direct feedback and long-term patterns to measure how viewers feel about a video.
These signals include post-watch surveys, user surveys, and long-term watch history analysis. Prompts like “Is this video satisfying?” give YouTube direct feedback. Over time, YouTube compares how viewers behave after watching a video, whether they continue watching, leave the platform, or return later.
Satisfaction is weighted more heavily than engagement alone because it predicts future behavior. A video can generate YouTube views and still perform poorly if viewers feel misled or disappointed. YouTube prioritizes videos that keep viewers happy, not just active.
3. Personalized recommendations and user context
YouTube does not rank videos the same way for everyone. It ranks videos for a particular viewer.
Personalization is based on individual watch history, video topics previously consumed, and recent search history. Device context also matters. Someone watching on a smart TV often sees longer videos, while mobile viewers are more likely to see YouTube Shorts.
Frequency of visits and session habits influence what appears next. If a viewer regularly watches similar content at certain times, YouTube adjusts recommendations to match that pattern. This is why YouTube recommended videos can feature heavily for one audience and barely be shown to another.
4. Long-term relevance and topic durability
Not all videos are evaluated on the same timeline. YouTube actively rewards long-term relevance.
Evergreen videos continue performing because they remain useful and searchable. YouTube resurfaces older videos when interest increases, when Google Trends data shifts, or when viewer behavior signals renewed relevance. This is common with tutorials, explainers, and long-form content.
Trending topics can drive fast visibility, but timeless topics build sustained watch time. In many cases, older videos outperform new uploads once the algorithm recognizes their durability.
5. Multi-language and global audience optimization
YouTube is a global platform, and its algorithm routes content across regions.
Auto-translation signals, closed captions, and metadata in multiple languages help YouTube understand who a video is for. Multiple audio tracks and accurate subtitles increase accessibility and expand reach to new audiences.
Videos optimized for multiple languages are more likely to be recommended internationally, especially when user behavior shows strong satisfaction across regions. This is increasingly important as YouTube recommendations become more personalized and globally distributed.
Where the YouTube algorithm recommends videos
YouTube recommends videos using different ranking systems for Home, Suggested, Shorts, and Search results.
When people talk about “the YouTube algorithm,” they usually imagine a single system deciding what gets seen. In reality, YouTube recommendations come from several interconnected systems, each designed for a specific purpose. A video can perform well in one place and poorly in another, depending on how it matches viewer intent in that context.
1. How the YouTube homepage algorithm works
The YouTube homepage is built around immediacy. It tries to predict what a user wants to watch right now, based on recent behavior rather than long-term intent.
To determine what each user wants to see, YouTube looks at:
- Recent watch history and search history
- What the viewer watched during their last session
- Time of day and device context, such as mobile versus smart TV
- Short-term user behavior patterns
Recurring watch patterns matter a lot here. If a viewer regularly watches similar YouTube videos at certain times, the homepage adapts. This is why the same video can appear repeatedly on one person’s homepage and never show up on another’s. The system is not ranking the video in isolation; it’s matching it to a particular viewer and their current mindset.
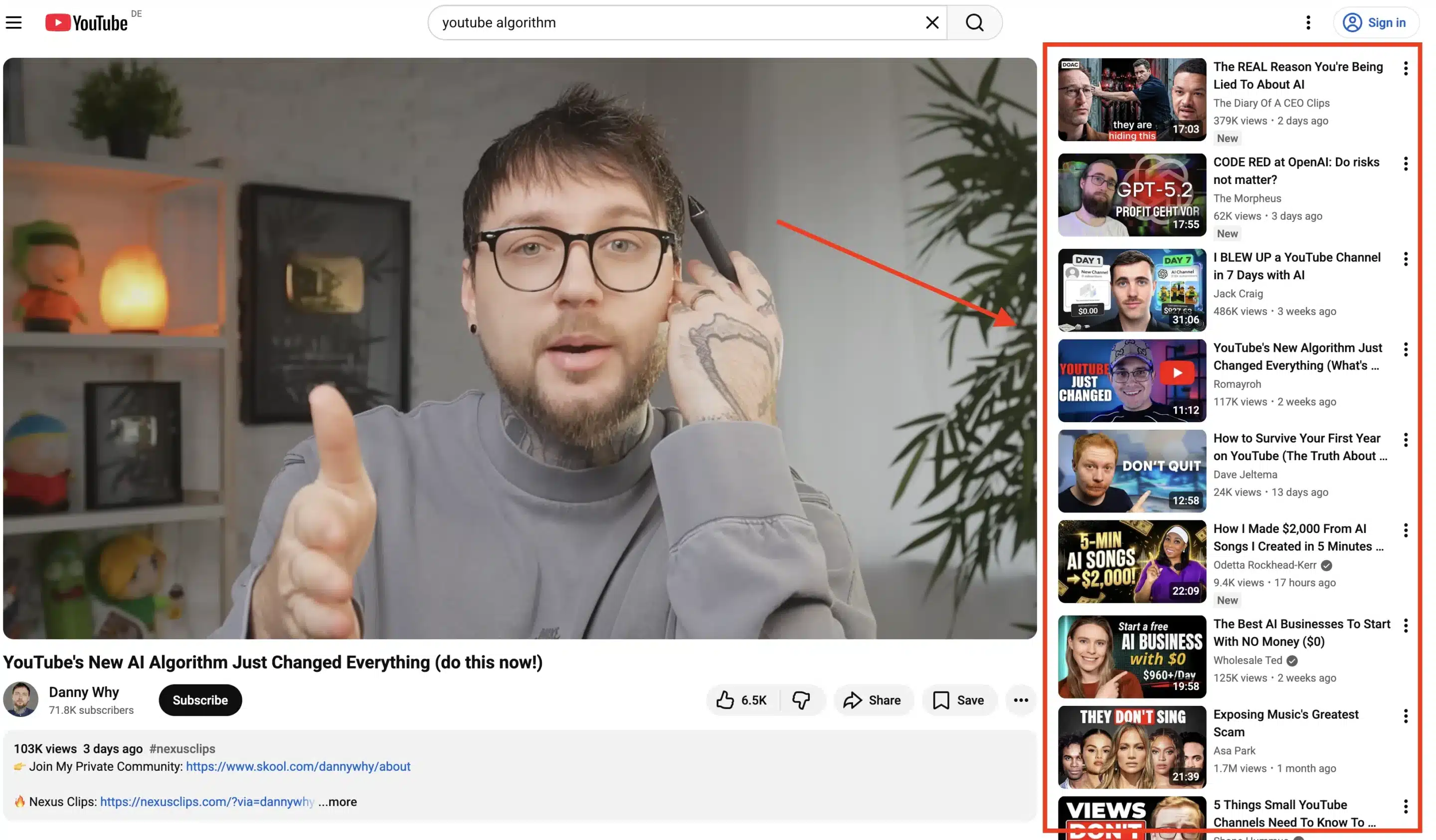
2. How the YouTube suggested videos algorithm works
Suggested videos are the highest-traffic surface on YouTube and the main driver of sustained YouTube video views.
Suggested relies heavily on affinity scoring, which looks at:
- Videos watched together in the same session
- Topic clustering across related videos
- Patterns tied to the same creator or similar creators
- How viewers move from the current video to the next video
If viewers consistently watch more than one video from the same creator, or move between related videos on the same topic, YouTube strengthens those connections. Over time, this creates powerful recommendation loops through related videos. This is why consistency in topic and format often matters more than chasing trends.
3. How the YouTube search algorithm works
YouTube Search behaves differently from Home and Suggested because it is intent-driven.
When ranking search results, YouTube focuses on:
- Search intent and relevance
- Relevant keywords in titles and video descriptions for YouTube SEO
- Captions, transcripts, and on-screen text
- Watch time and average view duration from search traffic
Search behaves more like Google search results than other YouTube surfaces, hence the name YouTube SEO. Clarity matters more than novelty. If YouTube clearly understands what a video is about and sees that viewers who find it through search stay to watch, it is more likely to rank and continue recommending that video over time, including resurfacing older videos when interest returns.
How the YouTube Shorts algorithm works in 2026
Shorts rely heavily on rapid satisfaction signals, completion rate, and rewatch behavior, and theyare a major part of YouTube’s success nowadays, given that they get 70 billion daily views.
The YouTube Shorts algorithm is built for speed. Unlike long-form videos, Shorts are evaluated almost immediately based on how viewers react in the first moments. YouTube is trying to determine whether a short video delivers value fast enough to keep viewers watching and whether it fits naturally into a viewer’s short-form consumption habits.
How the Shorts algorithm distributes videos
Every Short starts with testing. YouTube does not push Shorts broadly right away. Instead, it shows them to small initial test groups and closely watches behavior.
Key distribution signals include:
- Initial test groups, which help YouTube gauge early reactions
- Completion rate, which shows how often viewers watch the full Short
- Replays, which signal strong interest or clarity
- Swipe-through behavior, which shows how quickly viewers skip
Shorts that are watched all the way through, or replayed, expand into larger audiences. Shorts that cause viewers to swipe away quickly usually stop being pushed. This is one of the clearest examples of how quickly the algorithm tests and adjusts distribution.
How the YouTube Shorts algorithm ranks videos
Once a Short performs well in testing, ranking depends on speed and relevance.
YouTube looks closely at:
- Velocity, meaning early positive engagement relative to impressions
- Audience matching, based on watch history and past Shorts behavior
- Topic framing and clarity in the first 2 seconds, including visuals and on-screen text
Clarity matters more than creativity here. If viewers do not immediately understand what the Short is about, they are more likely to swipe. Shorts that lose viewers early rarely recover, no matter how strong the idea is.
Shorts and monetization changes in 2026
In 2026, retention plays a larger role in Shorts monetization. Completion rate and watch time influence RPM and eligibility more than raw views alone. Creators can earn between $0.01 and $0.06 for every 1,000 views.
Shorts that consistently hold attention are more likely to generate revenue and be included in broader recommendation cycles.
YouTube also increasingly encourages traffic flow between formats. Shorts are often used to introduce viewers to long-form content, guiding them toward longer videos from the same creator. When this flow works, Shorts act as discovery, while long-form videos drive deeper engagement and session time.
Tips for working with the Shorts algorithm
When you look at how the YouTube Shorts algorithm behaves in 2026, a few clear patterns emerge:
- Shorts perform best when the value is obvious immediately, since the algorithm heavily weighs early swipe-through behavior
- Videos with a clear topic and visual context in the first seconds are easier for the system to test and match to the right audience
- Completion rate and replays consistently signal stronger satisfaction than likes or comments
- Shorts are more likely to keep circulating when they fit naturally into existing viewing patterns rather than trying to appeal to everyone
- Shorts that connect cleanly to longer videos from the same creator tend to support broader channel discovery over time
These patterns reflect how YouTube evaluates Shorts quickly and at scale, using viewer behavior to decide whether a Short should continue being shown or quietly dropped.
How to improve your organic reach on YouTube in 2026
You can help the algorithm surface your content by improving discoverability, engagement, retention, and viewer satisfaction.
Once you understand how the YouTube algorithm works, improving organic reach becomes less about chasing hacks and more about aligning with how viewers actually behave. The goal is to make it easier for YouTube to understand your content, easier for the right audience to find it, and more satisfying for people to keep watching.
1. Work on visibility and discoverability
Visibility starts before anyone presses play. YouTube needs clear signals to understand what a video is about and who it is for.
Focus on:
- Doing keyword research aligned with real search intent, not trends for the sake of trends
- Writing clear, searchable titles that match what viewers are actually looking for
Designing YouTube thumbnails that clearly signal the topic and the value of the video
- Adding complete video descriptions and key timestamps to reinforce structure and relevance
- Including multi-language captions when possible to expand reach
- Posting regularly and scheduling content strategically
Posting regularly on YouTube increases your chances of being recommended, simply because you’re giving the platform more opportunities to test and distribute your content. When uploads are inconsistent, those opportunities shrink.
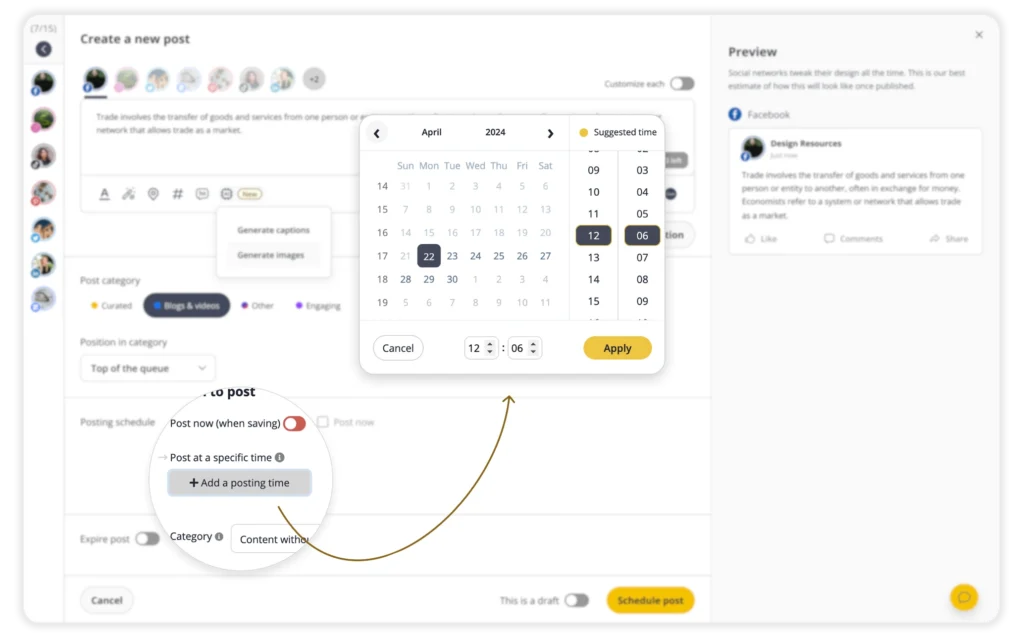
SocialBee is a YouTube scheduler that helps you plan, schedule, and publish both long-form videos and Shorts in advance. Instead of posting whenever you remember, you can stay active on a predictable schedule, which helps YouTube consistently surface your content to new viewers.
SocialBee also recommends the best times to post on YouTube based on your past performance. That means you’re not relying on generic timing advice. You’re publishing when your audience has already shown they’re more likely to click, watch, and engage. Together, planning ahead and smarter timing make it easier to stay visible, reach more people, and give each upload a better chance to rank.
Always post at the best times with SocialBee’s AI-powered suggestions
2. Increase engagement and build community
Engagement is not about maximizing comments at any cost. It is about meaningful interaction that reinforces satisfaction and repeat viewing.
Effective ways to support engagement include:
- Encouraging specific comment prompts instead of generic questions
- Responding consistently so viewers feel acknowledged
- Using Community posts to stay visible between uploads
- Posting when your viewers are most active
Replying to comments matters for engagement, but once videos start stacking up, keeping up with YouTube conversations becomes messy and time-consuming.
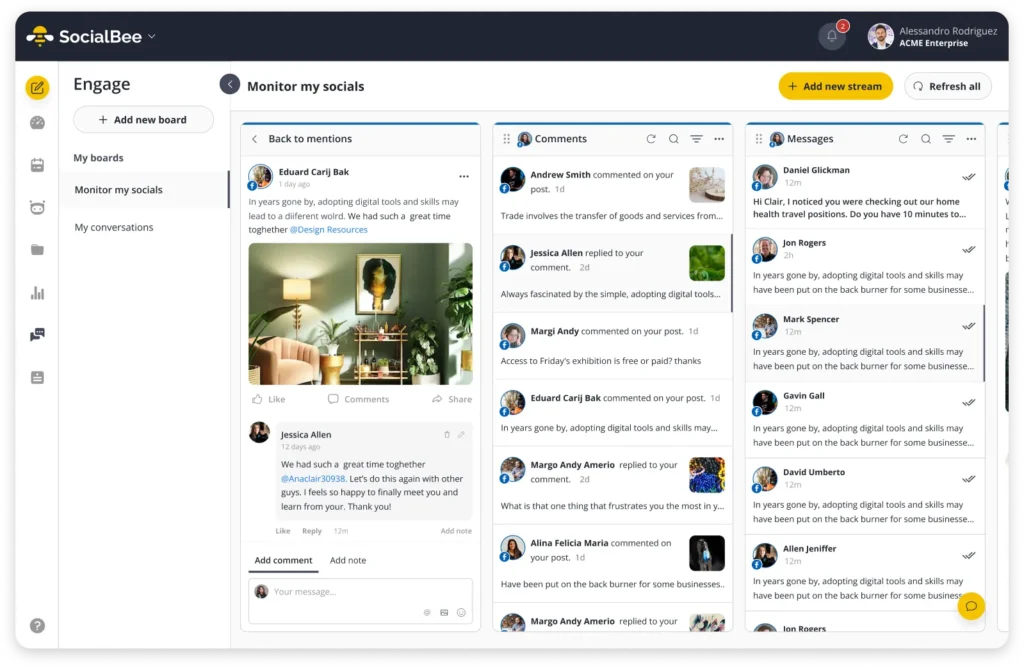
SocialBee brings your YouTube comments, plus DMs, mentions, and comments from your other social channels, into one social inbox. You can reply faster, stay consistent, and avoid missing those early comments that help build real momentum.
You can also schedule your first comment at the same time as your video. This is where you can add a specific question to spark replies, link to a related video to keep people watching, or drop a resource mentioned in the video without cluttering the description.
Stay on top of your social media interactions from one place with SocialBee’s unified inbox
3. Improve watch time and audience retention
Retention is one of the strongest signals YouTube uses to decide whether to keep recommending a video.
Key elements that support watch time include:
- Hooking viewers in the first 3 to 5 seconds of your YouTube intro so expectations are clear
- Structuring videos for continuous viewing instead of isolated segments
- Using chapters (timestamps) to give viewers a sense of progress
- Keeping energy and pacing consistent throughout
- Using end screens and cards to guide viewers to the next video
Videos that consistently hold attention are more likely to appear in suggested videos and keep circulating.
4. Optimize systematically with analytics
Improvement comes from patterns, not guesses. YouTube rewards creators who learn from how their content actually performs.
To learn and optimize based on your YouTube analytics, focus on:
- Studying retention graphs to see where viewers drop off
- Identifying repeat drop-off patterns across videos
- Comparing thumbnails and titles to understand click behavior
- Benchmarking video performance against your own past content, not other channels
A brief history of the YouTube algorithm
2005–2011: Optimizing for clicks and views
In YouTube’s early years, the algorithm focused almost entirely on clicks and raw views. Videos that attracted attention quickly were rewarded, regardless of whether viewers stayed. This led to widespread clickbait, misleading titles, and thumbnails that overpromised. The system was easy to game and often left viewers unhappy.
2012: Optimizing for watch time
In 2012, YouTube made a major shift toward watch time. Instead of rewarding videos that were clicked, the platform began favoring videos that were actually watched. This change reduced some harmful content and pushed creators toward making longer videos that held attention, but it still did not fully address viewer satisfaction.
2015–2016: Optimizing for viewer satisfaction
Around 2015 and 2016, YouTube introduced satisfaction as a core concept in a published white paper. User surveys, post-watch feedback, and long-term viewing patterns became part of ranking decisions. This was the point where viewer happiness started to outweigh pure engagement metrics. Videos that technically performed well but left viewers dissatisfied began losing reach.
2016–2025: Safety, demonetization, and advertiser protection
From 2016 onward, the algorithm expanded to include safety, brand suitability, and advertiser protection in its community guidelines. Demonetization systems, content classification, and policy enforcement became deeply tied to distribution. During this period, YouTube invested heavily in moderation tools, creator controls, and clearer policy signals, even when it meant reducing reach for certain types of content.
How YouTube changed in 2025
Before we dive in, quick context. We track YouTube updates weekly alongside changes from other major platforms. We send a curated newsletter with the most important news straight to your inbox, and we also maintain a weekly-updated report where everything is documented in one place. This is where we publish the latest news and make updates every week: https://socialbee.com/blog/social-media-news/
Now, here’s the simple version of what actually changed on YouTube in 2025.
If I had to explain it in one sentence, it would be this: YouTube stopped judging individual videos and started judging channels as a whole.
In previous years, you could win by chasing a spike. One strong video, one viral Short, one lucky recommendation. In 2025, that became much harder. The algorithm started paying more attention to patterns instead of one-off performance.
First, interaction matters more than views. Watching is no longer the finish line. YouTube now looks at what happens after someone presses play. Do people comment? Do they reply to each other? Do you show up and respond? With features like threaded comments, polls, quizzes, voice replies, and more visible community posts, YouTube is clearly prioritizing channels that feel active and social, not just channels that upload regularly.
Second, Shorts moved into the center of the system. In 2025, Shorts stopped being “extra content” and became a testing ground for the algorithm. YouTube uses Shorts to quickly figure out who your content resonates with. When viewers consistently engage with your Shorts, YouTube is more confident recommending your long-form videos and livestreams. Think of Shorts as fast feedback for the algorithm.
Third, AI became part of the infrastructure. Pre-upload checks, auto-dubbing, automatic quality upgrades, and AI tools inside YouTube Studio. All of these changes do the same thing: reduce friction and raise the baseline quality of content. From the algorithm’s point of view, that means clearer signals and less tolerance for low-effort, misleading, or policy-risky uploads.
Livestreams also changed their role. They’re no longer just live events. YouTube now turns livestreams into clips, Shorts, highlights, and community interactions automatically. When you go live, you’re no longer feeding one surface. You’re feeding several parts of the platform at the same time, which makes live content much more valuable to the algorithm than it used to be.
Finally, YouTube got better at understanding who you are and who you’re for. Handles replaced channel names, new viewer types like casual versus regular viewers were added, and category-based charts replaced the old Trending page. All of this helps YouTube place content more accurately. Channels with a clear topic, consistent format, and predictable posting rhythm are easier to recommend and easier to grow.
2026 and beyond: Personalization, multi-language optimization, and long-term viewer habits
By late 2025, YouTube’s updates made the platform’s direction clear. The algorithm in 2026 is shaped by a stronger focus on personalization, accessibility, and sustained viewer satisfaction rather than short-term performance.
Key shifts influencing the YouTube algorithm going forward include:
- Deeper personalization, with recommendations increasingly shaped by long-term watch history, session habits, and how a particular viewer interacts with content over time. “We’ve enabled the system to learn that different factors can have different importance in different contexts. Watch time may be more important in television versus mobile, or it may be more important in certain types of content like podcasts as opposed to music,” says Todd Beaupré, YouTube’s Senior Director of Growth & Discovery.
- Expanded multi-language support, driven by improvements to expressive captions, auto-dubbing, expressive speech, lip sync, and support for multiple audio tracks. (Source)
- Greater emphasis on accessibility, including wider use of closed captions and automatic quality enhancements that improve the viewing experience across devices.
- AI-assisted creation and editing tools, such as Generate Video, Edit with AI, and Extend with AI, which help creators produce clearer, more structured videos that are easier for the algorithm to understand.
- Stronger quality and policy signals, supported by improved pre-publish checks, clearer content detection systems, and expanded creator guidance in YouTube Studio. (Source)
- More detailed performance analysis, with separate analytics for paid versus organic reach, helping creators understand how videos perform over time, rather than chasing short spikes.
- Optimization for long-term viewer habits, where videos are evaluated based on whether viewers return, continue watching, and maintain trust in YouTube recommendations.
Together, these changes point to an algorithm that prioritizes clarity, accessibility, and consistency. In 2026, YouTube is less focused on aggressively pushing videos and more focused on recommending content that fits viewer preferences, language needs, and long-term enjoyment.
As for what type of content to create, YouTube CEO Neal Mohan says “The first and most important thing that I would say (about building a career on YouTube) is, think about what you are really, really excited about…the power of YouTube is that it’s not just an algorithm of your favorite meme of the week…it is about your face, you as the creator, and you build that because you talk about something authentically that your fans understand.”
Frequently asked questions
1. Does posting frequency affect the YouTube algorithm?
Yes, posting frequency affects the YouTube algorithm, but consistency matters more than volume. Regular uploads help YouTube identify active channels and build viewing habits, which can support recommendations over time. However, posting too often without maintaining quality can hurt performance, especially if videos lose viewers early.
The algorithm favors channels that publish on a sustainable schedule, keep viewers watching, and maintain strong retention, meaning consistent, high-quality uploads are more effective than frequent low-quality ones.
2. What is the 7-second rule on YouTube?
The 7-second rule refers to the critical window at the start of a video where viewers decide whether to keep watching or leave. During these first seconds, YouTube measures early retention, which strongly influences how widely a video is recommended.
If a video fails to hold attention quickly, it is more likely to lose viewers early and see reduced distribution. Clear topic framing, strong openings, and immediate relevance help videos pass this early evaluation phase.
3. How many views do you need to make $1000 a month on YouTube?
There is no fixed number of views required to make $1000 a month on YouTube because earnings depend on RPM, content type, target audience location, and viewer engagement.
Channels with higher-value audiences or longer videos can earn more with fewer views, while others may need significantly more traffic. In general, consistent watch time, strong retention, and advertiser-friendly content have a larger impact on revenue than raw view counts alone.
How SocialBee supports your YouTube content workflow
The creators who succeed in 2026 align with the algorithm’s real goal: long-term viewer satisfaction.
By this point, one thing should be clear. The YouTube algorithm is not something to outsmart or manipulate. It rewards creators who are clear about what they publish, consistent in how they show up, and relevant to the audience they serve. When videos set the right expectations, hold attention, and fit naturally into viewing habits, YouTube is more likely to recommend them over time.
Supporting YouTube with content across other platforms also plays a role. Promoting videos, Shorts, and Community updates consistently helps reinforce visibility without relying on one surface alone. If you want help planning your YouTube content alongside support posts across all your social channels, SocialBee is the social media scheduling tool for you.
Start your 14-day free trial and grow your social media presence across all major platforms from one place.